|
The Leaf View is used by botanists, registration authorities, and
compilers of regional flora to precisely identify the leaves, leaflets, and their
arrangement. |
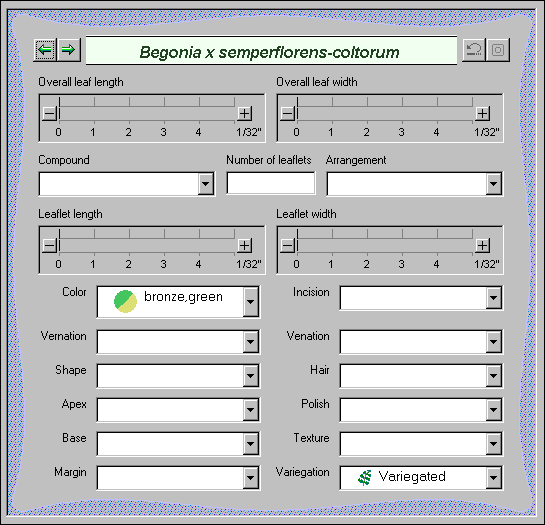
| Overall leaf length |
For simple leaves, this is the typical length from base to tip.
For compound leaves, this is the typical length of the full compound leaf. |
| Overall leaf width |
For simple leaves, this is the typical width across the widest portion
of the leaf. For compound leaves, this is the typical width of the
full compound leaf. |
| Compound |
This is the keyword simple for simple leaves. For compound
leaves this is variously one of the compound or pinnate
choices. |
| Number of leaflets |
For compound leaves only. This is the number of leaflets per leaf.
This value may be a simple number, like "5", or a range of values like
"11-15". |
| Arrangement |
A description of how the leaflets are arranged in relationship to each
other -- something like alternate, opposite, whorled, etc. |
| Leaflet length |
For compound leaves only. This is the typical length of a single
leaflet from base to tip. |
| Leaflet width |
For compound leaves only. This is the typical width of a single
leaflet across its widest part. |
| Color |
The color(s) of the leaves. |
| Vernation |
A description of how the young leaves are arranged before the bud opens.
Many possibilities such as convolute, contorted, rovolute, wrinkled,
and more. |
|
Shape |
The overall appearance of a leaf's shape -- possible values include:
crescent-shaped, fiddle-shaped, halbert-shaped, heart-shaped, kidney-shaped,
needle-shaped, sword-shaped, and many more. |
|
Apex |
The appearance of the leaf tip. Examples include: blunt, hooked,
mucronate, or retuse. |
|
Base |
The appearance of the leaf base where it attaches to the petiole.
Possibilities might be attenuate, cordate, hastate, truncate, and
more. |
|
Margin |
A description of the type of serration along the outer edges of the
leaf. Might be something like: curled, gnawed, crenated, sawed,
toothed, etc. |
|
Incision |
For deeply cut leaves, this is a description of how the divisions appear
-- something like lobed, palmate, split, and so forth. |
|
Venation |
A description of the pattern of veins within the leaf. Examples
include: divided, reticulated, pedate, peltate, ribbed, and more. |
|
Hair |
A description of the downy, hairy, silky, spiny, velvety, or woolly
covering on the leaves. |
|
Polish |
A description of the particulate covering on the leaves -- possibilities
include: dewy, dusty, greasy, powdery, slimy, etc. |
|
Texture |
A description of the leaf's surface texture -- leathery, papery,
spongy, waxy, etc. |
|
Variegation |
The location and appearance of discolorations and other markings on the
leaves: marbled, painted, spotted, striped, variegated, and so forth. |
|